This month, a new exhibition devoted to the art of the 17th-century painter Artemisia Gentileschi was to have opened at the National Gallery in London. Blue Guides was to have visited the exhibition and posted a review of it. That will now have to wait.
Artemisia Gentileschi features in many Blue Guides, notably the volumes covering Rome, Florence and Southern Italy. She was particularly fond of biblical and religious scenes with a tough female protagonist (Samson and Delilah, Salome with the Head of the Baptist, Judith and Holofernes). London’s National Gallery recently acquired a self-portrait of the artist in the guise of St Catherine of Alexandria, the saint who was broken on the ‘Catherine wheel’. The entry on Gentileschi in Blue Guide Florence says the following:
Gentileschi, Artemisia (1593–1652). Talented and independent, Gentileschi trained under her father, Orazio Gentileschi, an artist who owed much to Caravaggio. She worked in Rome but moved to Florence to carry out commissions for Cosimo II de’ Medici. Dramatic Caraveggesque chiaroscuro certainly suited Artemisia’s choice of subject matter. She had a particular affinity for the story of Judith and Holofernes (her most famous treatment of the subject is in the Uffizi). Legend relates this to the fact that Artemisia was raped as a young woman and that her assailant was never brought to justice.
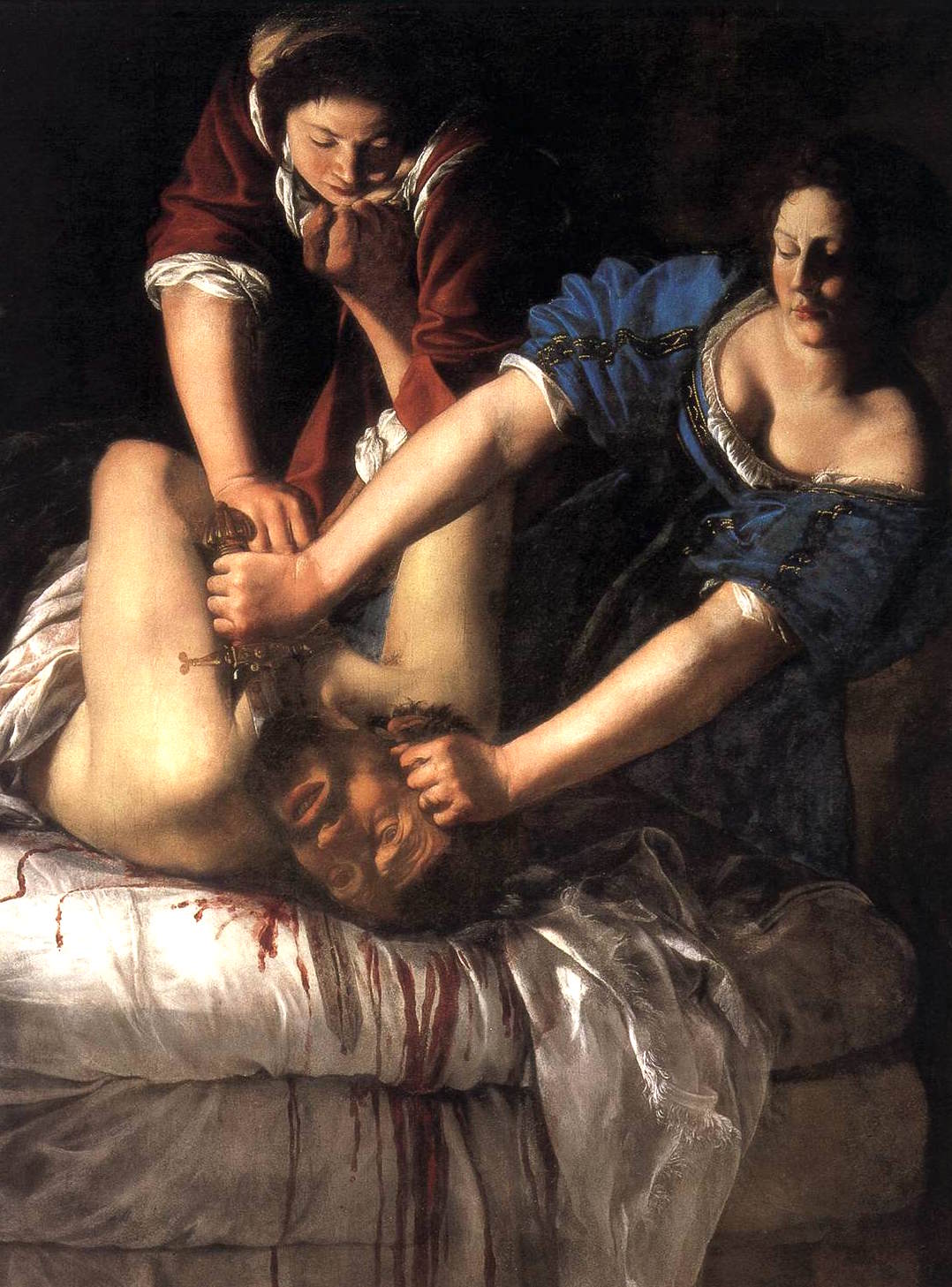
“Judith and Holofernes”. Museo di Capodimonte, Naples
According to the National Gallery, this story was no legend. Artemisia was indeed raped and her assailant, though found guilty, was never fully punished. Her attacker, Agostino Tassi, enjoyed a career in Rome producing painted decorations for a number of palazzi and as assistant to Claude Lorrain. Blue Guide Rome, in its Glossary of Artists, merely mentions him as a “painter known for his landscapes. In Rome he worked alongside a number of other artists.” Perhaps, after this London exhibition, we might feel tempted to say more.
Apart from the Judith and Holofernes in the Uffizi, there is another version of the same scene, in the Capodimonte museum in Naples. It is that version that is pictured above. And you can read more about the National Gallery’s planned exhibition on Gentileschi here.






